Food insecurity seldom comes to mind when considering Canada, a country recognized for its high standard of living. For those in the provinces, it may be shocking to hear the prices that those living in Northern Canada have to pay for such basic necessities. Yet food prices are so exorbitant that Northern Canadians, in particular the Indigenous communities that make up the majority of the population, are unable to sustain their families’ nutritional requirements. Government efforts to combat the issue are continuously insufficient and ineffective, exacerbating the structural inequalities faced by Indigenous populations in Canada.

The intersection of technology and education may not have been equitably galvanized, but the implementation of the platforms behind this intersection has been explored to the point where applications show promise in affecting change within the developing world; a high-quality education can help in fostering change in societies that suffer from marginalization. Through policymaking derived from the principle of egalitarian rational discourse, which is defined as a system of non-partisan individual and institutional political and social criticism of ineffectual structures for the good of all people, utilizing online education platforms at all levels, and responsible policymaking on the part of international bodies such as the UN and blocs such as Western Europe, both acting in concert with the developing world, the world stands to obtain long-term gains in its social and economic welfare.

Education is crucial to ensure human dignity of individuals. The right to education, as stipulated by UNESCO, entails primary education that is free, compulsory, and universal, and secondary education that is generally available, accessible to all, and progressively free. Yet, according to UNESCO estimates, 130 million girls ages 6 to 17 are out of school, and 15 million girls of primary-school age will never gain access to a classroom in their lives. Despite education being one of the most powerful tools in elevating the quality of life for marginalized individuals, it is often those very individuals that are subjected to conditions that restrain them from receiving this education. One of the most prominent global barriers to education for children is poverty. While poverty suppresses both male and female education, young girls experience distinct barriers that necessitate specific analysis, as exemplified in my case study of Nigeria.
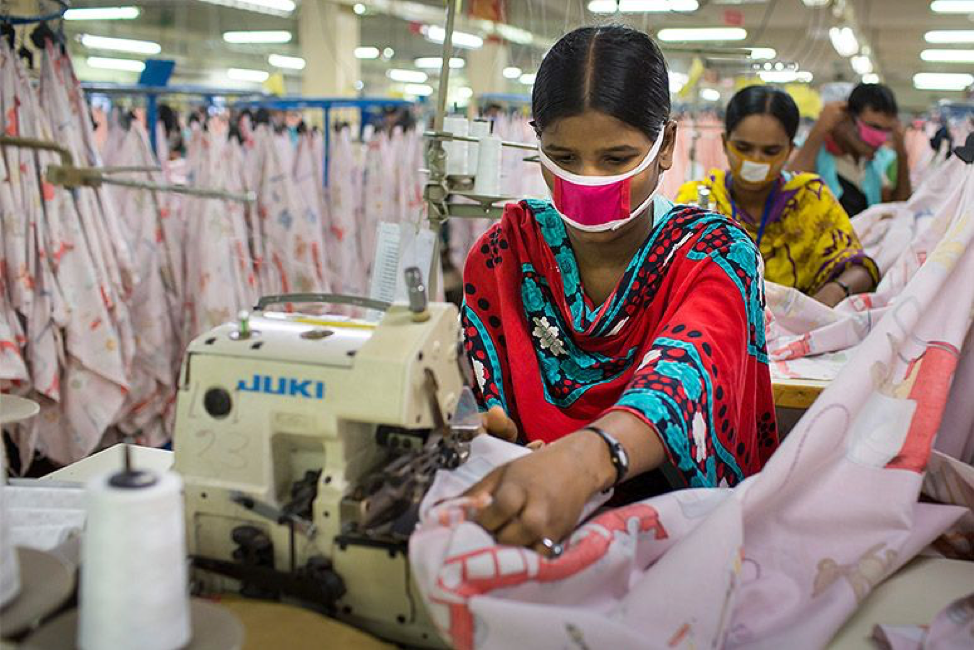

Prior to the nineteenth century, textile and clothing production relied primarily on made-by-hand methods. The Industrial Revolution of the early nineteenth century marked the transition to a new, more efficient manufacturing process in the Western world. Mechanized methods of manufacturing became widespread, resulting in cheaper and faster clothing production. As consumer prices fell, new apparel retailers emerged to cater to a growing demand for affordable garments, and to create employment opportunities. While the Industrial Revolution provided an incentive to increase profits, these motivations were also responsible for creating deplorable working conditions that exploited the absence of labor protection laws.

“The enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of health is one of the fundamental rights of every human being without distinction of race, religion, political belief, economic or social condition,” according to the World Health Organization. Health as a human right, however, has been widely overlooked as it becomes increasingly threatened by the effects of climate change. The health effects are not only diverse but also overwhelmingly negative and wide-ranging. These effects being both direct and indirect will therefore impact all individuals as well as economies worldwide. Populations are pressured to change their diets, rapid changes to ice, snow, and land result in more life-threatening accidents, and natural sources of drinking water are disappearing and diminishing in quality. It is estimated that between 2030 and 2050, there will be 250,000 additional annual deaths resulting from heat exposure, malaria, diarrhoea, and childhood malnutrition. The protection of the environment has thus become a crucial part of the contemporary human rights doctrine. According to the Office of the High Commissions for Human Rights, “Human rights law requires each State to do more than merely refrain from interfering with human rights itself; it also requires the State to undertake due diligence to protect against such harm from other sources.” The State has a duty to its people to safeguard their well being even if it means regulating environmentally harmful corporations and industries. Therefore, it is the evident inaction by global institutions, such as governments, relating to the exacerbation of climate change that violates the fundamental human right to health.
The coronavirus, or COVID-19, has quickly swept across the world, leading the World Health Organization to announce on Wednesday March 11, 2020 that the issue has become a pandemic. The new label means the rapidly spreading virus has already begun spreading to countries around the globe and will likely continue to do so. Originating in Wuhan, China, there are now over 150,000 people worldwide who have contracted the virus.

The United States’ presidential election is just around the corner. Some will be watching with excitement, others with fear. Either way, Trump will be the first president in American history to run for re-election despite being formally impeached by Congress. With the Trump administration’s four year term coming to an end, there has been no shortage of politically charged social media feuds or content for SNL.

Child marriages have been an unfortunate reality throughout the course of history. Until the 20th century, the average human’s life expectancy was approximately 50 years. Therefore, in an effort to expedite reproduction and the creation of families, girls were married off as soon as they hit puberty.
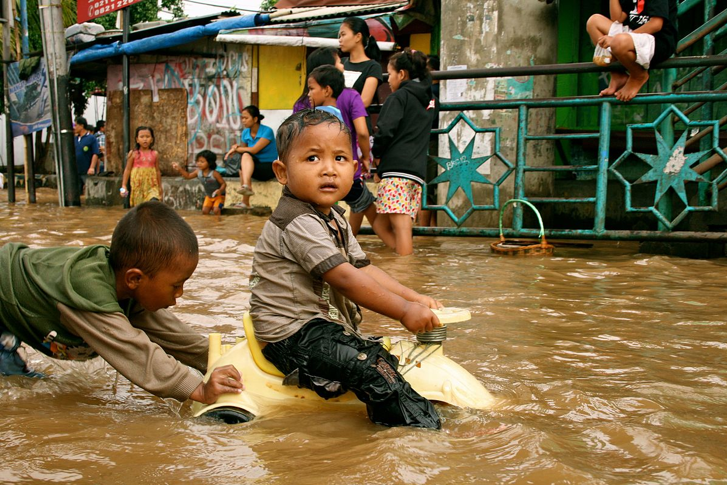

According to the World Health Organization, approximately eighty percent of the injuries, illnesses, and deaths resulting from climate change are in children. This stems from the increased presence of extreme weather events resulting from human-induced climate change such as droughts, floods, storms, and heatwaves that children are significantly more vulnerable too. These events directly affect people across the globe but it is the most blameless and innocent members of our communities who will suffer the greatest. For the first time in human history, we are in a state of climate emergency, requiring us to defend first and foremost those on the front line who are likely to suffer most from the effects of climate change: children.

Canada is currently experiencing nationwide protests from Indigenous groups in opposition of the Coastal Gaslink pipeline. The pipeline is roughly 670 kilometers, spanning across British Columbia; it was designed to ease the export of natural gas in the province. Although it may seem like a good idea to some, it is creating issues with Indigenous communities as the pipeline would cut directly through their land. The Wet’suwet’en Indigenous group is directly affected by this pipeline; however, Indigenous groups across the country, specifically in Ontario, have taken action to show their support.

