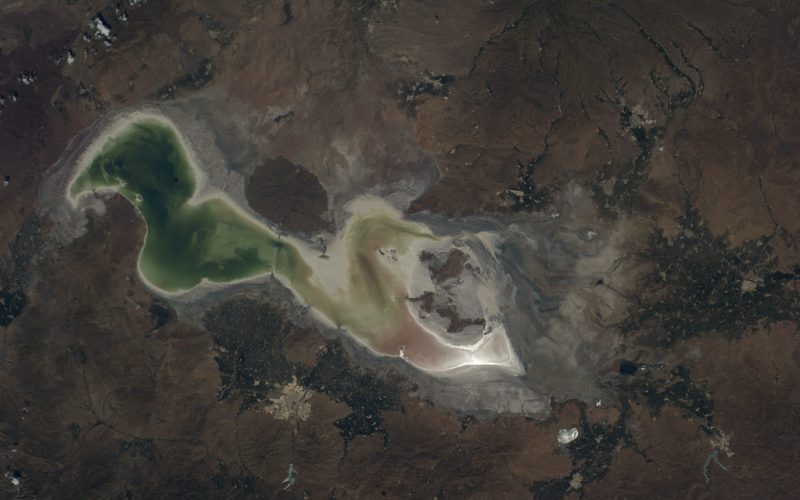
Over the past few decades, Iran has transformed from being the greenest nation in the Middle East to a country grappling with worsening air pollution and rising temperatures. Today, the […]
Latest
Behind the Spectacle: Mega-Sporting Events and Human RightsArctic Geopolitics and U.S. Foreign Policy: The Limits of Trump’s Greenland ProposalA Xenophobic Agenda: The Zero Tolerance Immigration PolicyThe Cost of Protest: The Potential Fall of the Iranian Islamic RegimeYour Like Is a Political Act – and Animals Are Paying for It
Monday, March 2